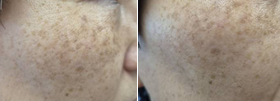
기미는 멜라닌 색소가 피부의 특정 부위에 과다하게 축적되어 생기는 비대칭적이고 불규칙한 갈색 반점입니다. 주로 여성에게 흔하며, 특히 임신, 피임약 복용, 호르몬 치료 중 발생할 수 있어 "임신 마스크"라고도 불립니다. 남성에게도 드물게 나타날 수 있습니다.
기미(melasma)는 피부과에서 흔히 접하는 색소침착 질환으로, 외관상 영향을 미쳐 심리적 스트레스를 유발할 수 있습니다. 이 보고서는 기미의 정의, 원인, 기전, 치료법, 예방법을 다양한 출처를 바탕으로 상세히 분석합니다.
기미의 특징
- 위치: 이마, 뺨, 코, 윗입술, 턱 등 얼굴 중심부에 대칭적으로 나타남.
- 색상: 연한 갈색에서 짙은 회갈색까지 다양.
- 형태: 경계가 불규칙하고 얼룩덜룩한 패턴.
기미의 정의
기미는 멜라노사이트(melanocytes)에서 멜라닌 색소가 과다 생성되어 피부에 갈색 또는 회갈색 반점이 생기는 상태입니다. 주로 얼굴에 나타나며, 표피, 진피, 또는 혼합형으로 분류됩니다. 기미는 양성 질환이지만, 만성적이고 재발 가능성이 높아 치료가 까다로울 수 있습니다.
기미의 원인 및 기전
기미는 여러 요인과 복합적으로 연관되어 발생하며, 주요 원인은 다음과 같습니다:
- 호르몬 변화:
- 에스트로겐과 프로게스테론 수치 변화(임신, 피임약, 호르몬 대체 요법)가 멜라노사이트를 자극해 멜라닌 생성을 촉진.
- 임신 중 발생하는 기미는 "임신 마스크(chloasma)"라고 불리며, 출산 후 호전될 수 있으나 완전히 사라지지 않을 수 있음.
- 자외선(UV) 노출:
- 자외선(UVA/UVB)은 멜라노사이트를 활성화해 멜라닌 생성을 증가시킴.
- UV는 염증 반응을 유도하며, 자외선(UVA/UVB) 같은 신호를 통해 기미를 악화시킬 수 있음.
- 유전적 요인:
- 가족력이 있는 경우 기미 발생 위험이 높음(특히 피부 톤이 어두운 Fitzpatrick 타입 III-VI).
- 특정 유전자(예: 멜라닌 합성 관련 유전자)가 기미 발생에 영향을 미칠 수 있음.
- 기타 요인:
- 염증(여드름, 피부염) 후 색소침착(PIH)과 유사한 기전으로 기미가 악화될 수 있음.
- 화장품, 약물(예: 항발작제), 갑상선 질환 등이 기미를 유발하거나 악화시킬 수 있음.
기전:
- 멜라노사이트가 자극(호르몬, UV, 염증 등)을 받아 티로시나아제 활성을 증가시키고, 멜라닌을 과다 생성.
- 멜라닌이 표피 또는 진피에 축적되며, 진피형 기미는 더 깊은 층에 색소가 침착되어 치료가 어려움.
- 플라스미노겐/플라스민 시스템이 염증과 혈관 투과성을 증가시켜 기미를 악화시킬 수 있음(트라넥사믹애시드가 이를 억제).
기미의 분류
기미는 색소 침착 깊이에 따라 다음과 같이 나뉩니다:
- 표피형: 멜라닌이 표피에 축적, 갈색 반점, 치료에 비교적 잘 반응.
- 진피형: 멜라닌이 진피층에 침착, 회갈색, 치료가 더 어려움.
- 혼합형: 표피와 진피 모두에 색소 침착, 가장 흔한 유형.
- 미분류형: 중심 안면형(이마, 뺨, 코) 또는 말라형(광대뼈 부위)으로 위치에 따라 구분.
기미의 치료법
기미는 완치가 어려운 만성 질환이지만, 다양한 치료법으로 관리할 수 있습니다:
- 자외선 차단:
- SPF 30 이상의 광범위 스펙트럼 자외선 차단제를 매일 사용.
- 모자, 선글라스 등 물리적 차단도 병행.
- 국소 치료제:
- 하이드로퀴논(2~4%): 멜라닌 생성 억제, 가장 효과적인 미백제. 장기 사용 시 피부 자극 가능.
- 트라넥사믹애시드: 국소(2~5%) 또는 경구 제제로 사용. 플라스민 억제를 통해 멜라닌 생성 감소.
- 아젤라산(15~20%): 항염증 및 미백 효과, 민감성 피부에 적합.
- 코지산, 비타민 C, 니아시나미드: 멜라닌 생성 억제 및 피부 톤 개선.
- 화학적 박피술:
- 글리콜산, 살리실산 등으로 표피를 벗겨내어 색소 제거.
- 민감성 피부에서는 자극 주의.
- 레이저 및 광치료:
- Q-스위치 Nd:YAG 레이저, IPL(광선치료)로 색소 분해.
- 진피형 기미에 효과적이지만, 부작용(염증 후 색소침착) 위험이 있음.
- 경구 치료:
- 트라넥사믹애시드(저용량): 염증 및 혈관 투과성 억제. 혈전증 병력자는 사용 금지.
- 항산화제(글루타치온 등) 보조적 사용.
예방법
- 자외선 관리: 매일 자외선 차단제 사용, 오전 10시~오후 2시 직사광선 피하기.
- 호르몬 관리: 피임약, 호르몬 치료 시 피부과 전문의와 상담.
- 피부 자극 최소화: 강한 스크럽, 자극성 화장품 사용 피하기.
- 정기적 피부 관리: 피부과 상담을 통해 조기 관리 시작.
안전성 및 주의사항
- 기미 치료 중 피부 자극, 붉은 기, 건조 등이 나타날 수 있으므로 보습제와 함께 사용.
- 레이저 치료 후 염증 후 색소침착(PIH) 위험이 있으므로 피부 톤이 어두운 사람은 주의.
- 경구 트라넥사믹애시드는 혈전증 병력이 있거나 흡연자라면 사용 금지.
결론
기미는 호르몬, 자외선, 유전적 요인 등으로 발생하는 색소침착 질환으로, 얼굴에 갈색 반점으로 나타납니다. 완치는 어렵지만 자외선 차단, 국소 치료제, 레이저 요법 등으로 효과적으로 관리할 수 있습니다. 꾸준한 예방과 피부과 전문의의 지침을 따르는 것이 중요합니다.
주요 인용 출처:
Melasma
American Academy of Dermatology: Melasma Overview
What is melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition that causes patches and spots, usually on the face, which are darker than your natural skin tone. While common, melasma can be mistaken for another skin condition. Board-certified dermatologists have the expertise required to give you an accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plan.
Is melasma contagious? No
Melasma is most common in women
Many women first see these blotchy patches and freckle-like spots on their face during pregnancy or when they start taking birth control pills. Melasma is so common during pregnancy that it’s sometimes called the “mask of pregnancy.”
For some women, the melasma goes away after their baby is born or they stop taking birth control pills.
- 호르몬 변화:
Melasma often begins during pregnancy
The blotchy brownish areas and freckle-like spots on this woman’s face are melasma, which first appeared while she was pregnant.
Women who have medium to dark skin tones are most likely to develop melasma. When melasma appears, it can cause tan, brown, grayish brown, or bluish gray patches and freckle-like spots. These usually appear on certain areas of face like the cheeks, forehead, chin, and even above the upper lip. While less common, melasma can develop on the arms, neck, or elsewhere.
What can get rid of melasma?
While melasma may go away on its own, this skin condition can also last for years.
If you dislike the discoloration on your skin caused by melasma certain treatments can sometimes help. Dermatologists recommend treating melasma sooner rather than later. It can be difficult to get noticeable results from treatment if you’ve had melasma for many years.
However, if you are pregnant, wait until you have your baby to treat melasma. If you use a melasma treatment that you can buy without a prescription, it can be difficult to know whether it’s safe to use during pregnancy. Also, melasma may improve and sometimes even go away after you give birth.
Is there a cure for melasma?
Treatments such as creams can help fade the discoloration, but treatments cannot make melasma go away forever. This skin condition can come back. It's common for melasma to return when you spend time outdoors without protecting your skin from the sun.
In fact, many people who have melasma say the dark spots and patches become more noticeable during the summer and fade in winter. For this reason, it is important to use sunscreen every day and wear a wide-brimmed hat to keep the spots from getting darker or returning.
Is melasma a type of cancer?
No, melasma is not a type of cancer. It’s also not a sign of skin cancer. Melasma differs from skin cancer in that it typically feels flat and appears on both sides of your face.
How can a board-certified dermatologist help with melasma?
If you have discolored patches or freckle-like spots on your skin, seeing a dermatologist can help ease your mind. A board-certified dermatologist can tell you whether melasma or another condition is causing the skin discoloration.
If you have melasma, a dermatologist can create an individualized treatment plan for you. Treatment usually begins with sun protection and creams that you apply to the melasma.
Many people who have a darker skin tone see a dermatologist for melasma treatment. In fact, treatment for melasma is one of the most common reasons that people who have a darker skin tone see a dermatologist.
Dermatologists understand that treating melasma in darker skin tones requires a different approach from treating melasma in lighter skin tones. For example, some melasma treatments can irritate darker skin, which can worsen melasma and make it darker.
Dermatologists know which precautions to take to prevent treatments from worsening melasma in darker skin tones. They also understand that it usually takes longer to see results from treatment if you have a dark skin tone.
It’s important to know that no matter your skin tone, melasma can be stubborn. Some people need a prescription strength-cream, procedure, or both.
If you use a non-prescription melasma treatment, dermatologists recommend using it for no longer than three to six months
If you don’t get the results you want by then, see a dermatologist for treatment.
A dermatologist can also help you with sun protection. To get results from treatment, you need to protect your skin from the sun every day.
Where does melasma develop on the body?
Melasma primarily develops on the face, usually on one or more of the following areas:
- Cheeks
- Chin
- Forehead
- Nose
- Above the upper lip
Occasionally, people develop melasma on their jawline, neck, arms, or elsewhere.
Wherever melasma appears, it causes blotchy patches and spots that can look like freckles. The color varies with a person’s skin tone and the severity of the melasma. In general, melasma is slightly darker than your natural skin color. Most people see various shades of brown. Melasma can look bluish gray in people with darker skin tones.
Melasma: an Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Abstract
Melasma is a common acquired condition of symmetric hyperpigmentation, typically occurring on the face, with higher prevalence in females and darker skin types. Multiple etiologies, including light exposure, hormonal influences, and family history, have been implicated in the pathogenesis of this disorder. Overall prevalence ranges widely at 1–50%, since values are typically calculated within a specific ethnic population within a geographic region. Histologically, melasma can display increased epidermal and/or dermal pigmentation, enlarged melanocytes, increased melanosomes, solar elastosis, dermal blood vessels, and, occasionally, perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates. Various topical, oral, and procedural therapies have been successfully used to treat melasma. Traditional topical therapies including hydroquinone, tretinoin, corticosteroids, and triple combination creams; however, other synthetic and natural topical compounds have also shown varying efficacies. Promising oral therapies for melasma include tranexamic acid, Polypodium leucotomos, and glutathione. Procedures, including chemical peels, microneedling, radiofrequency, and lasers, are also often used as primary or adjunctive treatments for melasma. Notably, combination therapies within or across treatment modalities generally result in better efficacies than monotherapies. This review serves as a comprehensive update on the current understanding of the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical and histologic features of melasma, as well as treatments for this common, yet therapeutically challenging, condition.
Keywords: Hyperpigmentation, Melasma, Pigmentary disorders, Skin of color
'건강' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MTS란? (0) | 2025.04.19 |
|---|---|
| '주름'이란? (0) | 2025.04.19 |
| 색소 침착의 기전은? (0) | 2025.04.19 |
| 홍삼, 그 힘의 비밀: 홍삼추출물 vs 홍삼발효추출물 (0) | 2025.03.10 |
| 락토바실러스(Lactobacillus)란? (0) | 2025.02.09 |